Price Plans for Fixed Pools of SIMs (FT-1014.007)
About this document
Scope
This document provides background information as well as a functional description of the FT-1014.007 Price Plans for Fixed Pools of SIMs standard feature. The described feature is supported from the release version 4.0 onwards.
Note
Price Plans for Fixed Pools of SIMs is a standard feature and does not require a special license.
This feature is part of the Price Plan Types functionality with number FN-1014.
Feature Availability
Feature Version | Available from | Summary of changes |
|---|---|---|
v1 | CMP Release 4.0 | Initial release |
Feature overview
Goals
The aim of the Price Plans for Fixed Pools of SIMs feature is to provide a Price Plan solution where the fixed total volume of the Price Plan to be distributed among multiple SIM Cards.
Functionality of the feature
Pool Price Plans are a special type of Price Plans, where volume is distributed among multiple SIM Cards instead of a single subscription. CMP supports two types of Pools: Flex and Static Pools.
Note:
The Pooling option is only available for Zone Price Plans.
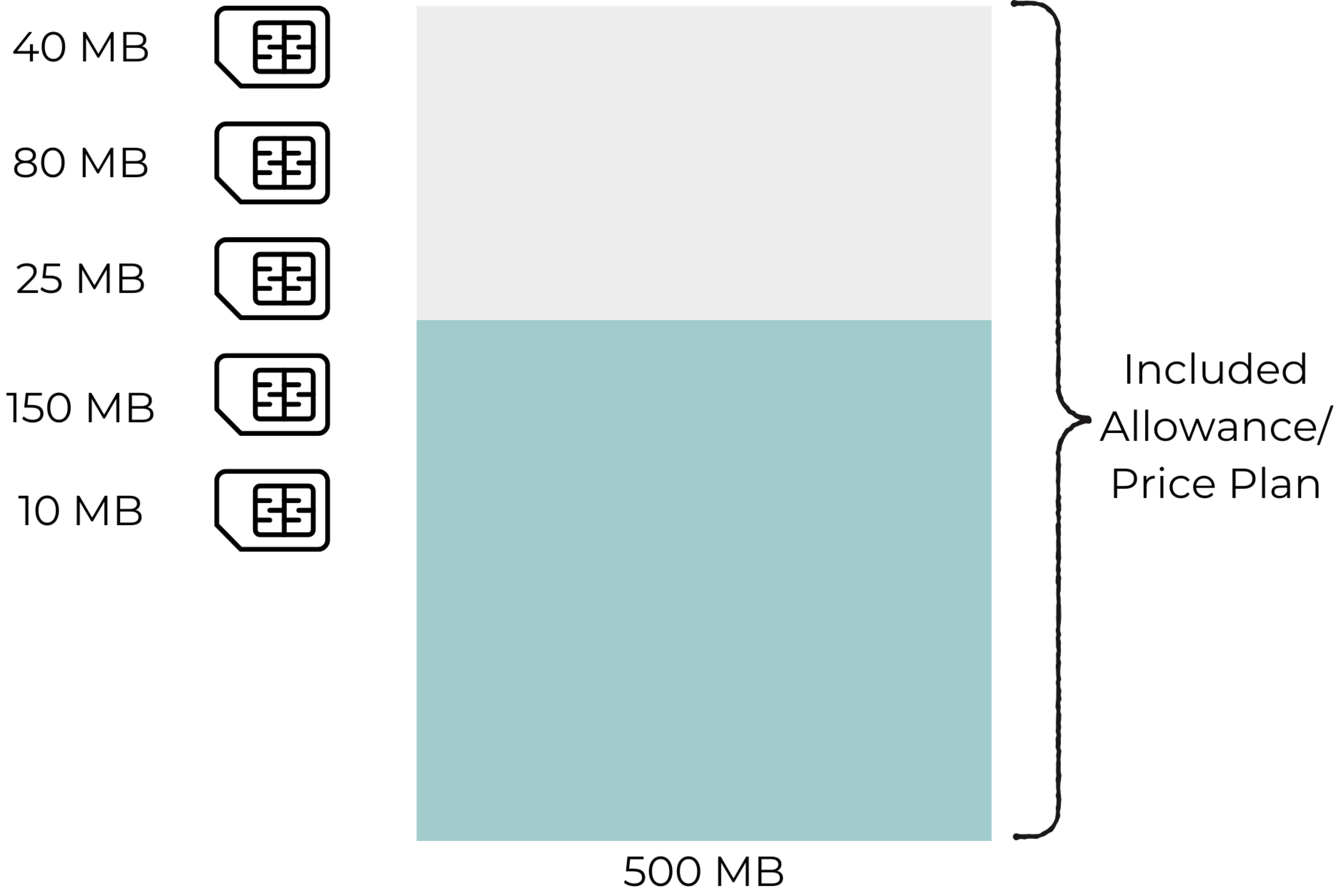
Static Pools
In a Static Pool, the entire pool of SIM Cards shared the total volume of the monthly included service of the Home Zone. The total volume of the Pool is fixed and does not depend on the number of SIM Cards in the Pool. In case the entire Pool is consumed then the additional usage will be charged at the defined overusage rate unless a Usage Stack is configured for the Pool.
Overusage Charge Type
Overusage Charge Type is configurable for Postpaid Static Pools in Zone Price Plans, defining whether overage rated or additional MRC will be applied once the allowance of the Pool is exhausted.
Overusage: Once the allowance of the Pool is exhausted rates defined in the Price Plan will be applied.
Fixed MRC Stack: Once the allowance of the Pool is exhausted additional MRC will be charged. When this option is set for the Pool, any overusage rate in the Price Plan will be set to zero (as overusage is covered by charging multiple MRC).
