CAS/SSO (FT-1008.006)
About this document
Scope
This document provides background information as well as a functional description of the FT-1008.006 CAS/SSO standard feature. The described feature is supported from the release version 4.3.5 onward.
Note
CAS/SSO is a standard feature and does not require a special license.
This feature is part of the User Management functionality with number FN-1001.
Feature Availability
Feature Version | Available from | Summary of changes |
|---|---|---|
v1 | CMP Release 4.3.5 | Initial release |
Feature overview
Scope
The scope of this Feature Description is to capture the new functionality of the CMP CAS/SSO Solution.
Unless mentioned explicitly, the features described are available in the current implementation. Features not available now are marked as ‘(planned for further CAS versions)’.
Goals
The CMP CAS/SSO Solution covers the following main functionality:
Centralized Identity and Access Management for all CMP Portals.
This replaces the local User Management in EP, RM, and BM.
Consistent context-based User Access Management across all CMP components (Web Applications and API access).
CMP Single Sign-On functionality for all CMP Web Applications (EP, RM, BM, and CMP CAS User Management Application).
User login procedure redirects to one common login screen that authenticates and authorizes CMP Users via the Central Identity Management (see above).
Implemented via state-of-the-art OAuth 2.0 authorization protocol for CMP.
Centralized API authentication/authorization for all CMP API domains (Enterprise Portal, Resource/Account Management, Billing Management APIs).
Implement OAuth 2.0 authorization mechanism for API access.
Maintain a basic authorization mechanism for API access.
Establish a CAS Server Infrastructure that utilizes Centralized Identity Management and enables the following core functionalities:
Integration capabilities to external IAMs (IdMs) via OAuth 2.0 Access delegation.
Support of state-of-the-art standards for user authentication and authorization.
Out of Scope
SSO integration to external IAM(s) via authorization federation, e.g. to LDAP or Active Directory.
Other authentication/authorization protocols than OAuth 2.0, specifically, SAML, OpenID, and OpenID Connect are not supported in the current version of the CMP CAS.
Other User Database integrations than CMP internal CAS Database, Directory Services like LDAP or Active Directory are not supported.
Preconditions & Assumption
Optional feature for SSO Integration to external IAM(s) is available.
Functionality of the feature
Apereo CAS Server
The CMP CAS Solution is built around the Apereo CAS Server reference implementation of the CAS Protocol (see https://apereo.github.io/cas/6.2.x/index.html for a detailed description).
The following diagram from the Apereo website (see https://apereo.github.io/cas/6.2.x/planning/Architecture.html) shows which components of the Apereo Standard Architecture are used to fulfill the goals of the CMP CAS solution listed above:
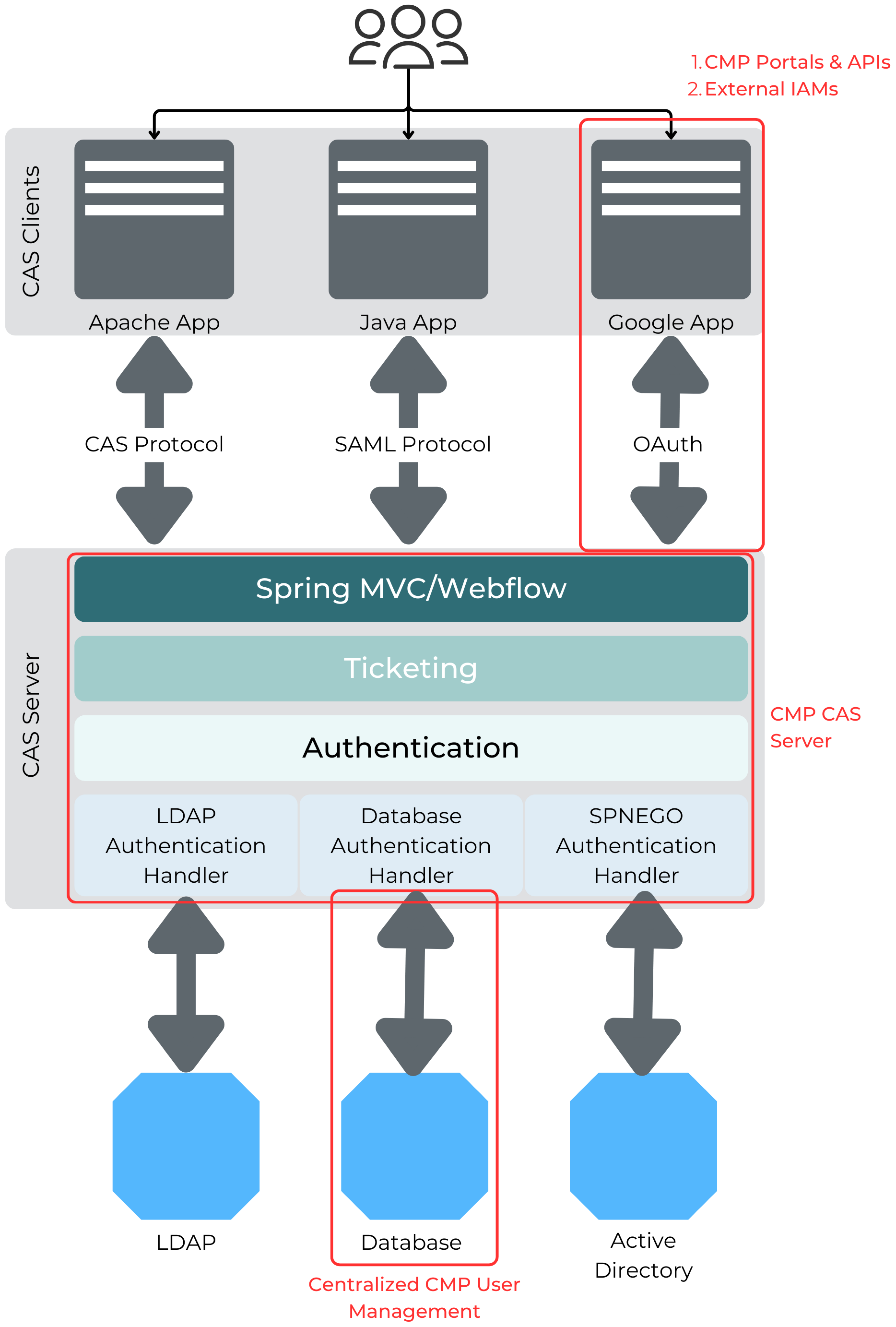
Mapping of Apero CAS architecture to CMP CAS solution
The standard OAuth 2.0 protocol integration capabilities are used to enable SSO for all CMP Portals and API access. In this case, the CMP Web Applications act as CAS Clients.
The same standard capabilities are used to delegate authentication/authorization via OAuth protocol to external IAMs to support various SSO integration scenarios.
In this case, the standard authentication flows have to be adapted to enable the different user authentication/authorization scenarios.South-bound the Apereo CAS Server is integrated into a Central CMP CAS Database.
The following elements supported by the Standard Apereo CAS framework are currently not used by the CMP CAS Solution and correspondingly out-of-scope (see as well mapping in the diagram above):
Other protocols than OAuth 2.0, specifically, SAML, OpenID, and OpenID Connect are not supported in the current version of the CMP CAS.
Other User Database integrations than CMP internal CAS Database, Directory Services like LDAP or Active Directory are not supported.
If required in the future CMP CAS features might be extended - based on the native capabilities of the Apereo CAS Implementation.
CMP CAS Solution Design
As a summary, the CMP CAS Solution consists of the following components:
The CMP CAS Server based on the Apereo CAS Implementation Framework (see above),
the Central CMP CAS Database replacing the Local User Information stored in EP, RM, and BM, and
the CMP User Management Application to manage the Centralized User and Access Information.
The following diagram sketches the different components and related interactions that make up the CMP CAS Solution:
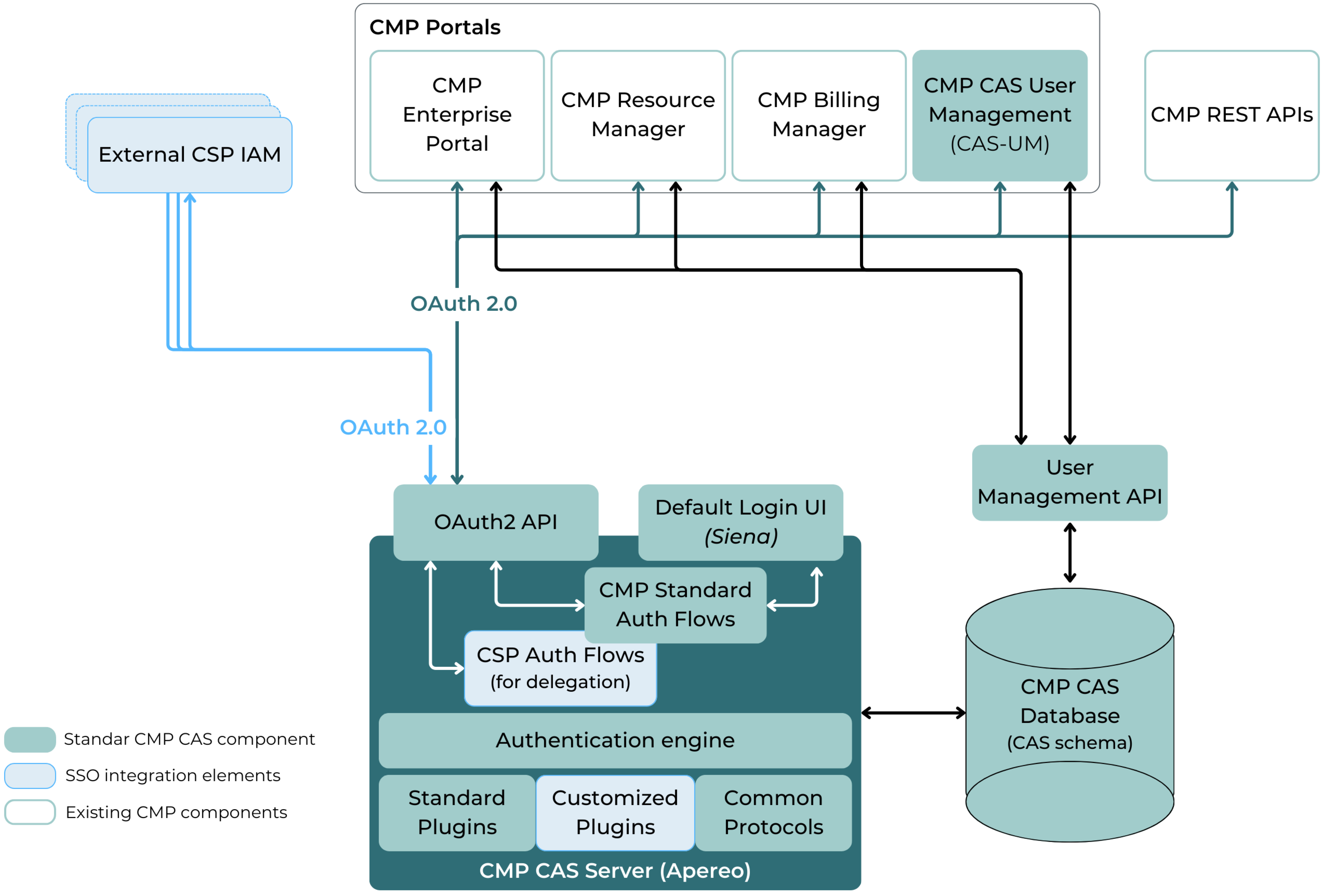
CMP CAS Architecture overview
The following chapters provide a more detailed overview of the functions and characteristics of the various components of the CMP CAS Solution.
CMP User Management Application
The MAVOCO CMP CAS User Management Application is a web application (based on the Siena GUI design) that is used to manage Users, User Groups, Access Rights, Templates for Access Rights, and for User Notifications. It can be used for CMP Software Components starting with the CMP version 4.3.5 or higher.
Basic Concepts of CMP User Management
CAS User:
A CAS User is a person who utilizes the CMP Software (via UI a/o API). The User Is related to an Identity that can exist In the CMP CAS System or can be provided by an external System (SSO integration via authorization delegation). → See the definition of delegated and local users below.
CAS users have the following life-cycle:
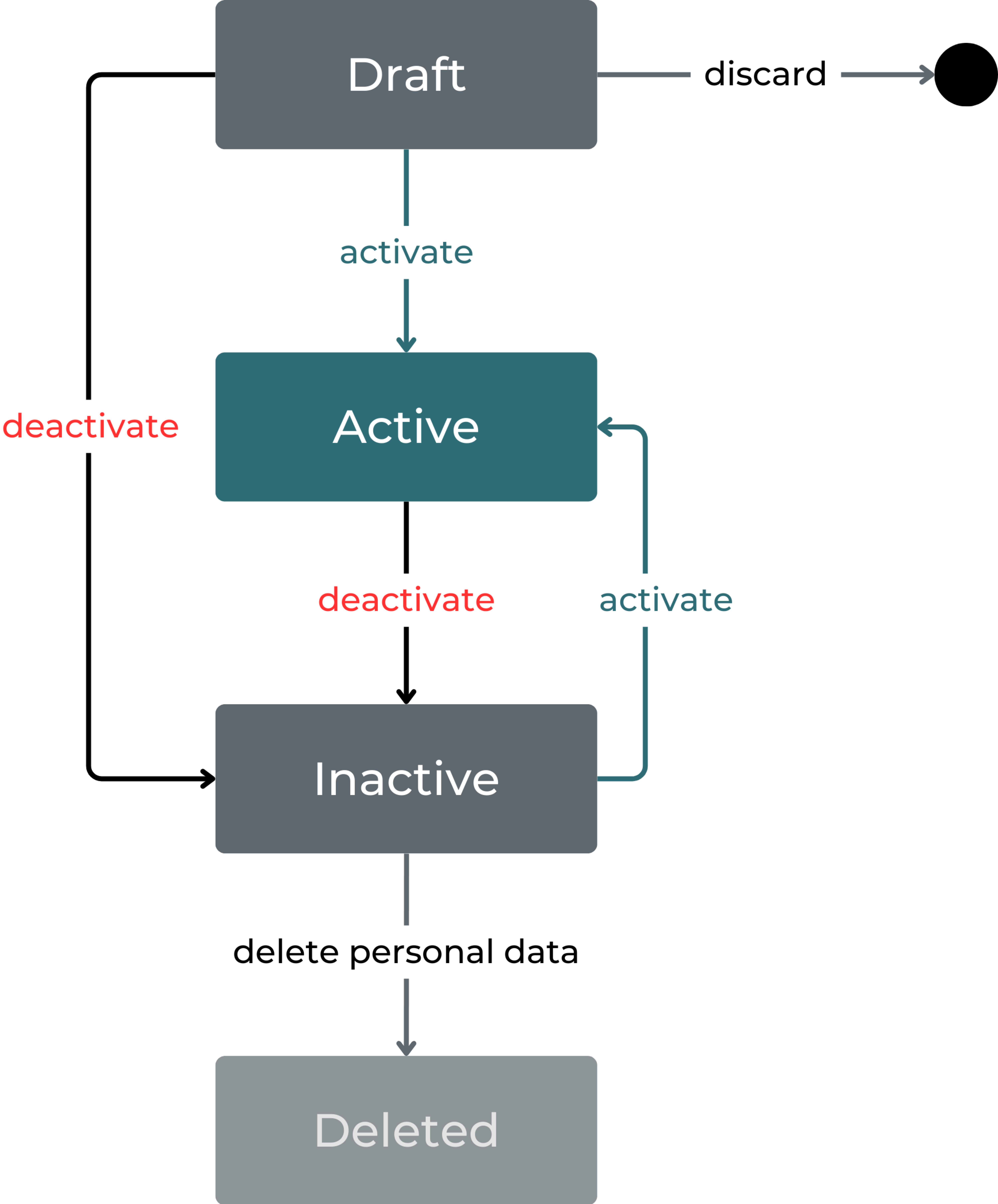
The described states have the following meaning:
Draft: Information entered for the user in this status can still be discarded, the User will be removed from the database. Draft users are not allowed to access any CMP module.
Active: Once activated a user is entitled to access CMP systems according to its authentication and authorization settings.
Inactive: Deactivation of a user blocks its access to CMP modules. Inactive users can be set back to Active at any time, given the user - performing the reactivation - has sufficient access rights.
Remark: Deactivation of a user will take effect with the next login attempt or after token timeout (in case the user is logged-in during activation)
Deleted: Deleting a user anonymizes its data without deleting the user in the database. References to the anonymized user record, e.g. in the audit log information are kept. Deleted users cannot be re-activated.
Users in this status can be archived after a given retention period (planned for further CAS versions)
Local and Delegated users:
In an SSO integration scenario, Users - before getting authorized by the CMP CAS solution - may be authenticated via an external IdM (Identity Management System). Such users are defined as ‘Delegated’.
In contrast, standard CAS Users authenticated and managed completely in the CAS environment are called ‘Local’ Users.
User Domain:
Allows to group users in different categories with similar behavior and semantic. By default the following 2 user domains are set-up (can be extended)
CSP
ENTERPRISE
Users belonging to the same user domain share the following information:
Applied rule for user creation: The following diagram depicts the standard restrictions for user creation related to the standard User Domains:
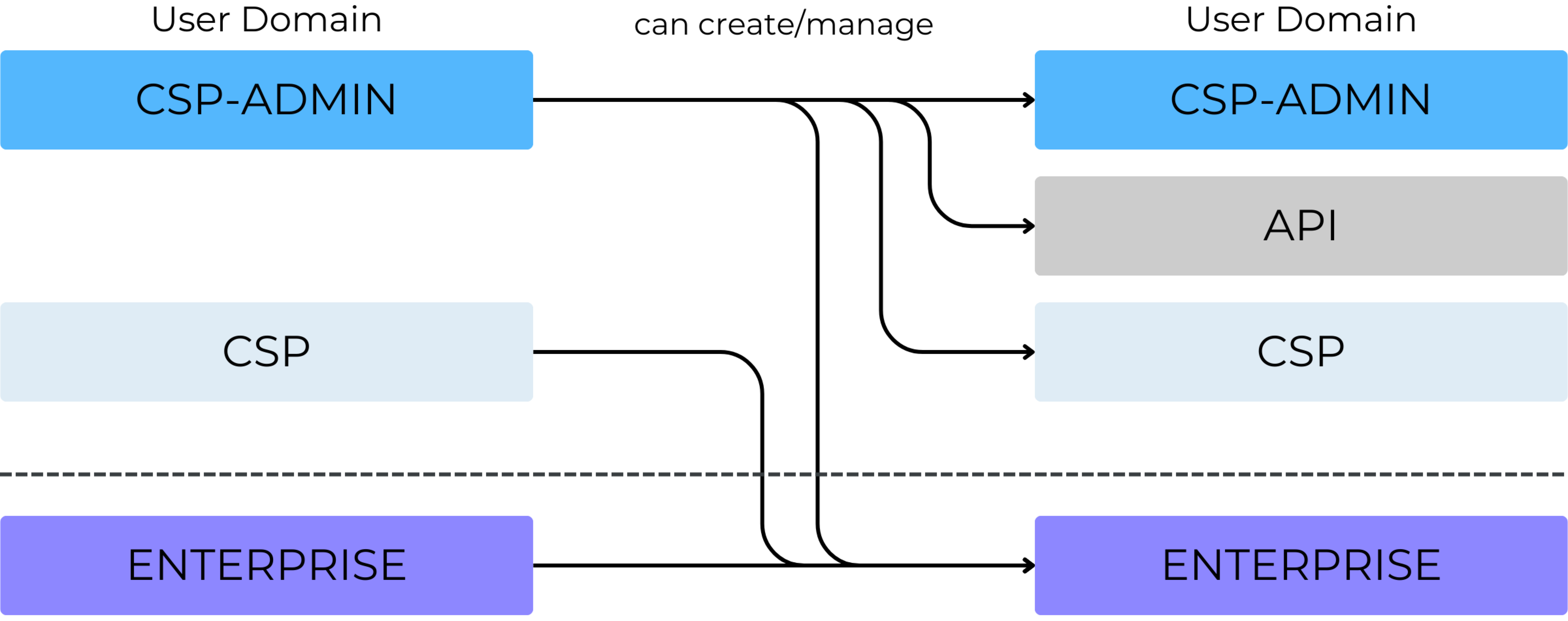
Whether a user is local or delegated (or federated - for future use), this information is a property of the user domain
The (User) Context:
The main task of the Siena CAS application is to give a User right to functions and access to objects.
Functions are controlled via ACL, there is a corresponding ACL for each function. These are maintained by MAVOCO and the list of ACL is expanded with every new feature.
Access to objects depends on the context of the User. Users can be
CSP Users who have access to almost all objects,
Account Users that can only see their own objects
Users of Groups or even Customers of the Accounts who can only see a subset of the Account data.
The following Context Types are supported by CMP CAS, which also form a hierarchy:
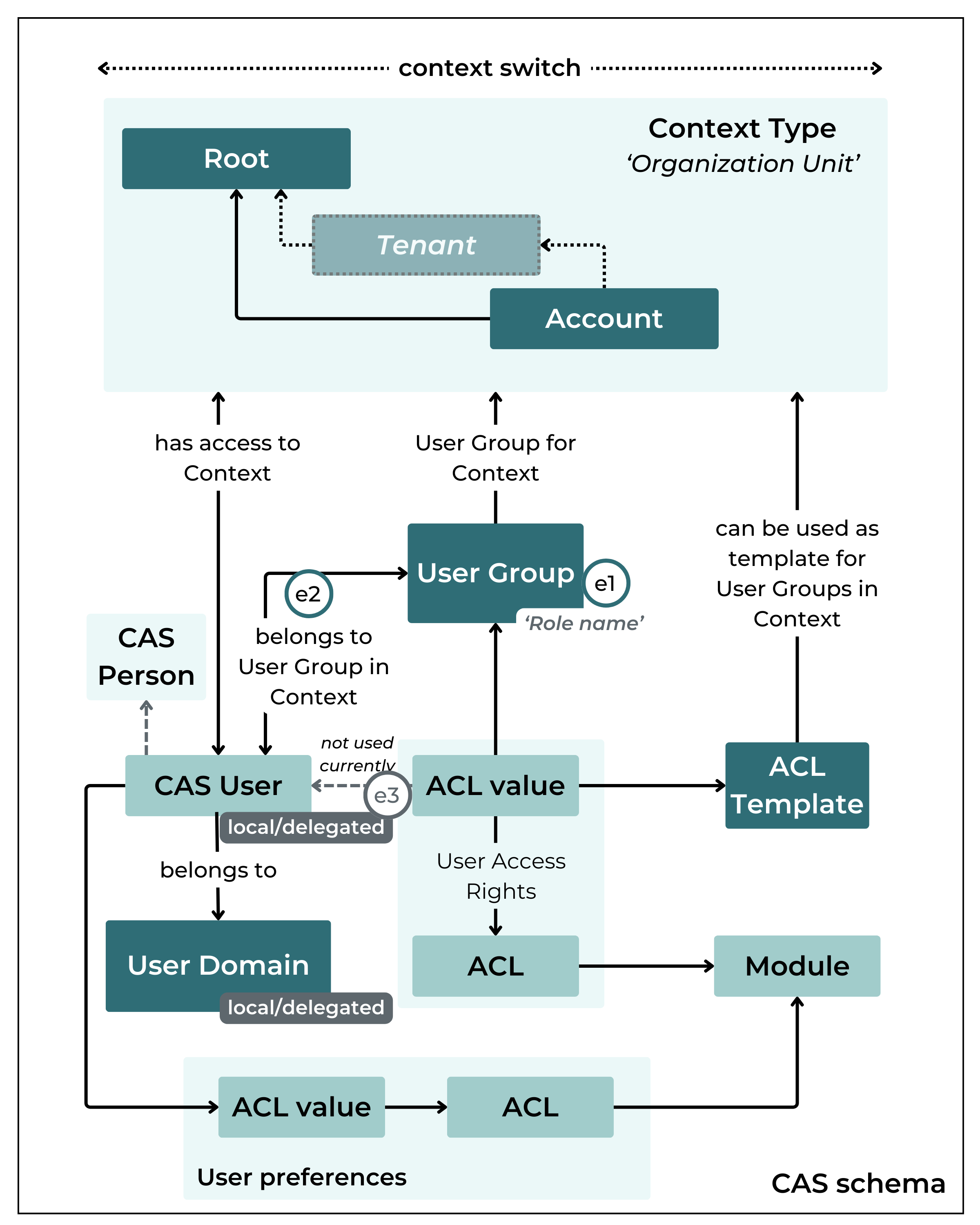
Root: Marks the highest/root level of the Context hierarchy. Remark: The name of this Context Type has been changed to ‘Root’ (formerly called ‘CSP’) to avoid confusion with the CSP User Domain
Tenant: for MVNOs, Resellers or to supporting MNO own access hierarchies: (planned for further CAS versions)
Account: Remark: Sub-Accounts are on the same context levels, there is no distinction between Accounts and their Sub-Account from a Context Management point of view
Account-Customer (planned for further CAS versions)
A CAS User can have different Roles and can have access rights (ACL) in more than one Context.
Context Switch:
As an example, a User can be an Administrator both for Account A and Account B. The CMP software will not show all Objects in one data grid. If a User needs to switch from one Account to another Account, a Context Switch needs to be done. Accordingly, the content of the software will be adapted.
Access Rights and ACL:
For each CMP module (EP, RM, BM, and CAS-UM) there is a predefined list of access rights that allow to specify functional rights for CMP users.
Examples (module / access right name / data type):
portal / ‘SIM - Price Plan Modify’ / boolean: Allows a user - if set to true the user - to modify Price Plans for SIM in the EP (= module)
cas / ‘CAS users - Create or Modify’ / boolean: This access right allows to change and create new users on the CAS-UM module
Remark: Although ACL (Access Control List) literally defines a list of access rights, in the context of CMP it's used both for a list of rights and one single right (= access right) in the ACL
Access Rights (ACLs) within a module are grouped into categories to show functional dependencies between rights and to simplify search processes. Examples:
Category ‘SIM Cards’ in module ‘portal’ to group all access rights related to changes on a single SIM Card
Category ‘User Management’ in module ‘cas’ to group all access rights related to user Management functionality
Remark: There is a specific Type of ACLs, which are not used for managing user access rights. Although using the ACL mechanism, ACLs in the category ‘User Preferences’ are specifically used to store the user’s preferences in relation to a module (e.g. ACL portal / 'Dashboard Panels' / Text for storing the user-specific dashboard settings in a text field). Correspondingly ACLs in this category are not visible when defining ACL templates, User Groups, or retrieving Effective User Rights for a user.
The vast majority of access rights are from type Boolean, thus they simply indicate whether a right is granted to the user (value = true) or not (= false). Currently, there is one Access right from type ‘Text’ defined (Module: ‘portal’ / Category ‘API’): ‘API IP Allow’. For this ACL the following rules apply:
if not assigned the user CAS user will not be able to perform API calls at all. This follows the general logic for Boolean user rights: if not assigned the corresponding right is considered as false = not allowed. Consequently removing a once granted IP range can be achieved by removing the 'API IP Allow' access right (supported in the newest CAS-UM and EP version).
If assigned
with value ‘0.0.0.0/0’ means no validation is performed - user with this value will be able to use API calls
with an IP range different from '0.0.0.0/0' the corresponding validation will be performed. This means only users with IP-address within the given range will be allowed to perform API calls
Rules for CMP Module Access (status v.4.3.5):
The following CMP Modules support Users with access on Root and Account level: Enterprise Portal (EP) AND CAS-User Management (CAS-UM)
That means any CAS user can access these Modules regardless if he’s assigned to Root or one or many Account Contexts.
The functions and data that are visible to the user will depend on the access (for example, root user can see all account, account user only specified accounts)
In contrast, the CMP modules Resource Manager (RM) and Billing Manager (BM) currently only grant access to CAS users having access to the Root level. Users assigned on Account level are not supported and don’t get access to these modules.
Additionally for Billing Manager access the Access Rights ‘bmModuleAccess’ must be enabled for the respective CAS user
Effective User Rights:
To answer the question, if a User has access to a specific function (described by an ACL), in a given context, the evaluation of several user rights related concepts (see below) is required. The result of the evaluation - computing the rights according to the defined evaluation steps - defines the Effective User Rights of a given User in a given Context. Remark: Effective User Rights only make sense in combination with a context, Effective User Rights without context are useless.
Effective User Rights are 'evaluated' (calculated) every time a) the user logs in to a CMP module or b) the context of the user has been switched.
In order to support mapping of user role definitions in external IdMs to CAS access right concepts, the effective rights calculation for delegated users comprises more evaluation steps (see e.g. step e1 below) than for local users. Steps only applicable for delegated users are marked accordingly in the following section.
Effective User Rights Evaluation steps
To calculate the Effective User Rights of a CAS User in a Context the following steps are performed:
e1 (only applicable for delegated users) - In case the user is provided with an external role name (via external authentication flow) AND the Context has a User Group assigned with a matching ‘Role name’, transfer the User Group settings to the Effective User Rights of the user. Remark: To take User Group settings into account it is sufficient that role names match, the user does not have to be assigned to the User Group (in contrast to step e2).
e2 - In case the user is assigned to one or many User Groups in the Context, write the settings to the Effective User Rights list. For more than one User Groups the evaluation will follow the alphabetical order (User Group Name), later access rights will overwrite earlier User Group rights - or access rights remaining from step e1 (only for delegated users).
e3 - (not used currently) Finally, access rights assigned to CAS User directly overwrite Effective User Rights calculated in steps e1. Remark: Experience shows that the functionality to define user-specific access rights - deviating from context Access Policies or User Group definitions - was rarely used. Thus, this option has been disabled for the time being.
Generally all access rights not assigned on a level (User Group, User) are considered as false = not allowed. Consequently, each access right not appearing in any of the evaluation steps is considered false when calculating the Effective User Rights for a user.
Remark: A user right not assigned is as well called ‘inherited’ as it ‘inherits’ its values from previous evaluation step (if applicable). So 'Inherited' is NOT an ACL value but an indication that the ACL is not assigned, thus the value is by default considered as false (see above).
Context Access Policy:
Assigning user access rights directly to a context (Root or Account) defines a standard set of access rights, the so-called Access Policy. The Access Policy allows to limit the available access rights for a given Context to a restricted subset, providing additional filter functionality when calculating effective user rights (planned for further CAS versions).
User Groups:
User Groups have been a well-known concept in CMP and have been transferred to the CMP CAS solution.
By assigning a User to a User Group the user ‘inherits’ the Group's access rights. This allows to define a local (context-specific) combination of access rights that can be used by all users in the related context.
It is possible to assign a user to more than one User Group in the respective context. In this case, the Effective User Rights will be calculated in alphabetical order (see above).
ACL Templates:
Assigning Access Rights to Users, User Group, or a context (as Access Policy) individually is very time-consuming, as there are already hundreds of different ACLs defined. To simplify the management of user rights the concept of ACL Templates has been introduced. It replaces the one-by-one assignment and setting of ACLs - as required in the past - by copying the ACLs of the ACL Template in one step.
With ACL Templates a CSP can easily assign pre-defined combinations of access rights in a short time. It enables the definition of standard sets of access rights and accelerates the allocation of rights.
During the usage of an ACL Template the related access rights are copied to the corresponding entity (User Group or Context). This means any subsequent change to an ACL template does not impact the settings of any User Group or context the Template was used with.
The following logical data model shows the entities described and how they are related to each other:
User Management Use Cases
The following table lists all User Management Use Cases that are supported by CMP User Management Application (CAS-UM) and the relationship to corresponding functions in the various CMP Portals.
User Management Use Case | Description | Transferred from Portal(s) |
|---|---|---|
Manage CAS Users |
| Enterprise Portal (EP):
Resource Manager (RM):
Billing Manager (BM):
|
Password Management |
| Enterprise Portal (EP):
Resource Manager (RM):
Billing Manager (BM):
|
Manage Contexts and User Groups (Organization Unit Access) |
| Enterprise Portal (EP) & Resource Manager (RM):
|
Manage ACLs |
| Enterprise Portal (EP) & Resource Manager (RM):
|
Manage ACL Templates |
| No existing functionality in CMP Portals. |
Manage Messaging Templates |
| Enterprise Portal (EP), Resource Manager (RM) & Billing Manager (BM):
|
CMP CAS Server
SSO Integration Aspects
The CMP Software can exist completely without an external IdM system. However, in many cases, the CSP has an existing IAM and especially wants to offer internal users a single-sign-on user experience.
The integration of external parties like customers makes the whole process much more complicated and fragmented. In most cases, portals for private customers do not play a major role in systems like our CMP, however, the CSP could have existing portals for business customers.
Another use case could be the merging of different CMP Platforms, for example, customers who have an Account in Jasper could also register with the same identity to our CMP Software.
CMP CAS Solution currently supports SSO integration via authentication delegation (via OAuth 2.0) and SSO integration to external IAMs via authorization federation is out-of-scope.
SSO integrations based on CMP CAS solution
The following diagram summarizes
the required CMP CAS components,
the related CMP CAS standard functionality (see CMP CAS Architecture), and
the functionality that requires integration services for an SSO integration.
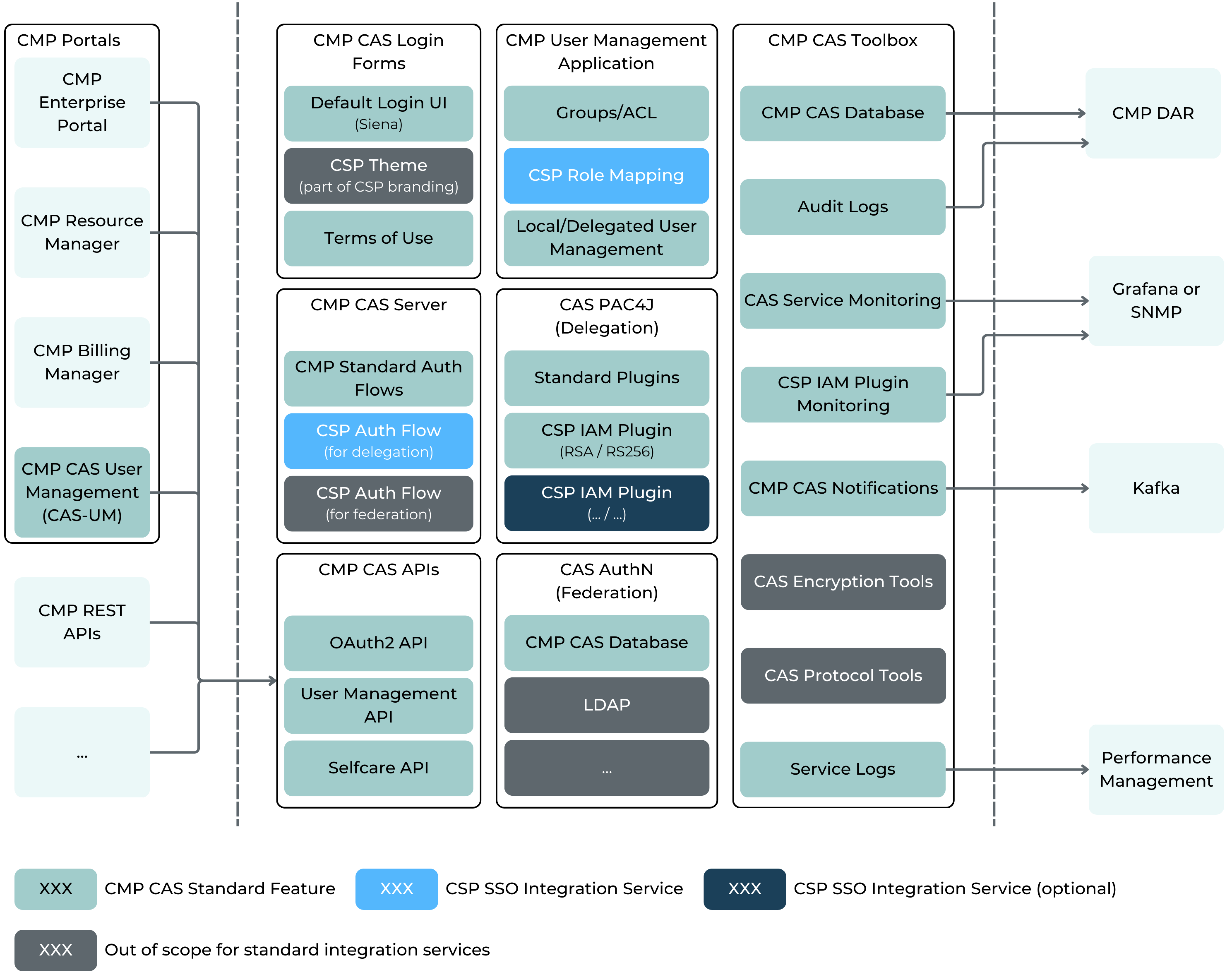
CMP CAS SSO integration components
SSO Integration Services | CMP CAS Component | Purpose | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|
CSP Auth Flow (for delegation) | CMP CAS Server | CMP Provides default login flow only (see below) based on CMP User Database and CMP Login Screens. For CSP having its own process, CSP CAS Service flows have to be configured. | This is the main customization service for integration to external IAMs. |
CSP Role Mapping | CMP User Management Application | CMP provides its own User and Access Rights Management web application (='CMP User Management Application'). Initial setup is required to enable access to CMP Services:
| This is required if external IAM is based on authorization via Roles. |
CSP IAM Plugin | CAS PAC4J (Delegation) | CMP CAS uses the PAC4J framework to delegate authentication. Currently supported token encryption and signature verification (RAS/RS256):
| The PAC4J project provides some standard plugins for the most common platforms (see https://www.pac4j.org/docs/clients/oauth.html). |
CMP Portals
The introduction of a centralized CMP CAS Solution supporting SSO requires the following migration/development tasks on each CMP Portal:
Implementation of SSO for each Portal.
Replacement of the local User Management functions by access to the centralized User Management functions (via User Management API).
Migration of the local User Information to the centralized CMP CAS Database (only EP and RM in the first version).
Single Sign-On for all Portals (EP, RM, and BM)
The following diagram shows the standard sequence of OAuth API calls for SSO implementation on each Portal (see as well the diagram for CMP CAS Architecture above):
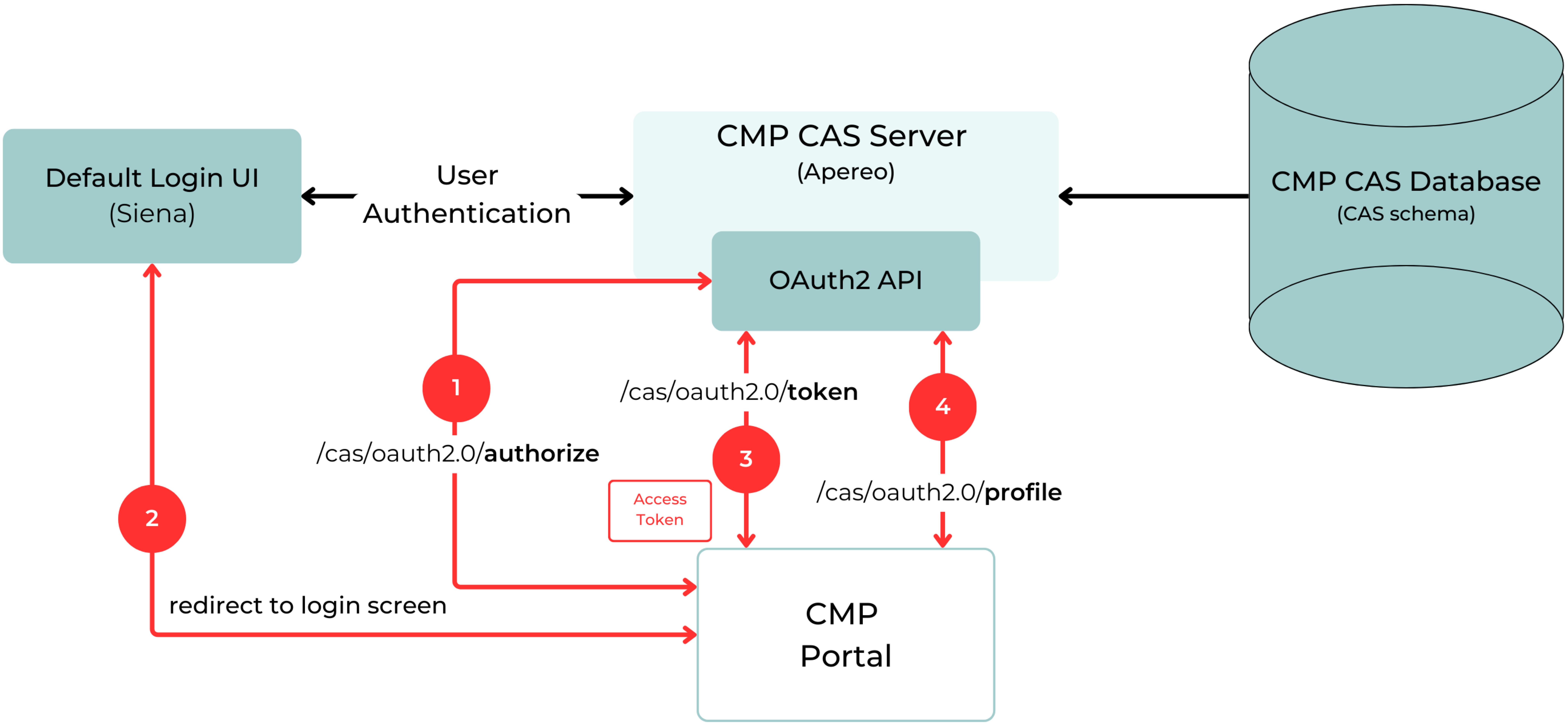
Standard CMP SSO authentication flow
Authentication via the local login screen is replaced by redirection to the common SSO login screen for the CMP CAS Solution.
This replaces local authentication and authorization by CAS SSO and is applicable to all CMP Portals (EP, RM, and BM), also including the CMP User Management Application.
Portal Use Cases related to CMP CAS
Local User Management functions are replaced by access to the centralized User Management (via User Management API).
In the first version, this will only be implemented for Enterprise Portal and Resource Manager, Billing Manager will follow in a later version.
As a general rule, all functionalities currently available via local User Management must be available after migration to the CMP CAS Solution (either via CAS User Management or via adapted EP or RM Portal functionality).
Note: This does not imply that the application and the corresponding UI will NOT change.
Some functionalities for managing Users locally are replaced by corresponding functions in CMP User Management Application.
Some functions will only be available in read-only mode.
Portal Use case | Impact of CMP CAS Solution |
|---|---|
Context Switch | Enterprise Portal (EP):
Resource Manager (RM) & Billing Manager (BM):
|
Create Groups (SIM-Groups) in EP | Enterprise Portal (EP):
Resource Manager (RM) & Billing Manager (BM):
|
Create User Groups | Enterprise Portal (EP) & Resource Manager (RM):
|
Manage Users in Portal | Enterprise Portal (EP):
Resource Manager (RM):
Billing Manager (BM):
|
'Forgot Password' on Enterprise Portal Login Screen | Enterprise Portal (EP):
Resource Manager (RM) & Billing Manager (BM):
|
Show Profile | Enterprise Portal (EP) & Resource Manager (RM):
Billing Manager (BM):
|
Change Password | Enterprise Portal (EP) & Resource Manager (RM):
Billing Manager (BM):
|
Reset Password | Enterprise Portal (EP):
Resource Manager (RM) & Billing Manager (BM)
|
User Management APIs exposed for external use
Read CAS User
Create CAS User
Assign Person to User
Create User Group
Change User Group
Assign User to a User Group
2FA
Two-factor authentication provides an additional layer of security for User accounts by requiring a second step of verification at sign-in. In addition to using the login name and password to log in, the User has to enter a one-time password sent to them via SMS or email, depending on the configuration of the respective User.
CMP supports two channels for 2FA: SMS and email. SMS and email as 2FA token channels can be set independently from each other. The possible configuration options are:
SMS only,
email only, and
SMS and email.
Note that this capability is dependent on integration into SMS and/or email server.
General 2FA settings provided by CMP can be overwritten for specific Users in the User Profile by the Admin User with a specific User Right. The available values for User 2FA settings are the following (depending on the available features):
disabled,
SMS,
email, and
SMS and email.
2FA token SMS is sent to the User’s phone number specified in the User Profile. Filter mechanism allows to block SMS in case the User MSISDN doesn’t match a given pattern. In case the token SMS is blocked, corresponding feedback is displayed during the login process.
2FA token email can be sent in CMP default language (i.e. English) or the User’s preferred language that is defined in the User Profile. The email is sent to the User’s email address specified in the User Profile.
The minimum length of the sent 2FA token is 6 digits and the lifetime of the token can be configured on the CMP instance.
CMP instance can be configured to only send OTP token when the User logs in for the first time; otherwise, the token is sent with each login. CMP stores the timestamp of the first successful User login in order to allow that.
